Chainbase in-depth analysis: Raised $15 million, the largest full-chain data network enabling Crypto and AI to empower each other
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Chainbase in-depth analysis: Raised $15 million, the largest full-chain data network enabling Crypto and AI to empower each other
Chainbase aims to integrate all blockchain data into a unified ecosystem, becoming the largest trusted, stable, and transparent data source in the AGI era.
By TechFlow

The current crypto market is gradually entering a consolidation phase. As narratives quiet down and existing projects offer little innovation, where can new Alpha opportunities be found?
Looking outward, the AGI era wave has arrived; looking inward, AI remains the dominant narrative across the crypto space throughout the year, attracting both attention and liquidity.
However, you now need to look more carefully within the AI sector for "structural" opportunities:
Focusing on the three fundamental elements of AI — computing power, algorithms, and data — the first two have already produced leading projects such as Render Network, IO, and Bittensor, with many similar projects crowding into this now highly competitive space; data-focused projects are mostly evolving toward DePIN.
The true opportunity lies in effectively utilizing native Web3 on-chain data, which remains a treasure trove for discovering Alpha.
And early-stage capital, known for its sharp instincts, has already started voting with their feet:
Major recent funding rounds have reemerged. Chainbase, a project in the data sector, announced a $15 million Series A round led by Matrix Partners, with participation from a strategic investment by an internet company, Hash Global, Folius Ventures, JSquare, DFG, MaskNetwork, Bodl Ventures, Bonfire Union Ventures, and other well-known institutions.

Capital flows often signal anticipation of future narratives and confidence in specific projects. So why is Chainbase attracting such investor interest?
TLDR: The largest full-chain data network, an open data stack technology
Here are some key highlights for those who want the quick summary to rapidly understand Chainbase.
-
A higher-dimensional product: When discussing on-chain data, common associations include smart money analysis, dashboard building, and data querying. Chainbase is an infrastructure (Infra) product operating at a higher dimension—applications like these can be built on top of it, but Infra enables far more than just that.
-
The largest full-chain data network: This higher-dimensional positioning begins with its defining feature—the largest "full-chain data network"—aggregating and processing any data from any blockchain across the fragmented crypto landscape, even off-chain data, forming a data goldmine awaiting discovery;
-
Solid project background/team/backing: Chainbase serves over 15,000 developers and 8,000 projects, handling 500 billion full-chain data calls. Its team members come from top-tier tech companies with expertise in data-related fields. Beyond the investors mentioned above, it also receives architectural support from premier partners (Eigenlayer provides economic security, Cosmos provides consensus security).
-
Self-consistent logic behind the data network: Unlike public chains that follow the model of "first build the chain, then find use cases," Chainbase initially targets developers and regular users by providing high-quality data, and builds its own data network once the ecosystem and use cases mature.
-
Crypto-native AI large language model: Unlike most industry projects that simply wrap around GPT, Chainbase's self-developed Theia AI model is trained on native, high-quality on-chain data and supports multimodal interaction, showing potential to become a foundational cornerstone for Web3 × AI.

When all on- and off-chain data can be contributed and fulfill their value, and when everyone can leverage data plus AI to find suitable applications,
Web3 begins to have its own On-Chain Data Infrastructure. The market’s imagination expands dramatically, and the scent of Alpha becomes palpable.
Just as oracles were pivotal for DeFi, data is crucial for AI. When full-chain data performs its "dance of intelligence," will the crypto stage witness a new breakthrough performance?
Grab your early access pass—we’ll take you on a sneak peek: a preview analysis of Chainbase, the largest full-chain data network, covering its product mechanics, application scenarios, AI capabilities, and economic model.
On-chain data: the underutilized "dark knowledge"
To understand Chainbase and its business logic, we must first grasp the value of data.
As early as 2017, The Economist’s cover story declared, “Data has replaced oil as the world’s most valuable resource.” Now in 2024, with the rise of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), this most valuable resource is being efficiently mined and utilized by AI:
OpenAI extracted 570GB of data from 45TB of raw data to train GPT-3—massive, fast, real-time, and structured. And that’s without mentioning GPT-4. Both data quality and quantity continue to grow, enabling superior AI performance.
In contrast, on-chain data in the crypto world remains underutilized.
Today, Web3 data lies scattered in isolated corners. Most crypto projects merely make this dormant data stand up—using traditional database models to index and query on-chain data, or using Text-to-SQL methods to convert queries into SQL code and return results...
The on-chain data you use is neither intelligently analyzed nor capable of real-time feedback, nor can it comprehensively traverse every corner of every chain in the crypto world and systematically deliver knowledge and insight like GPT.

We can only mechanically answer objective questions about "what is," but intelligent guidance on "how to act" remains missing. In other words, while on-chain data appears transparent, it is actually still sleeping "dark knowledge."
It lacks intelligence, proactivity, creativity, and decentralization.
When leveraging data, most crypto projects fail to fully activate community agency.
Crypto enthusiasts are full of hidden talent and could create templates based on their own research needs to demonstrate how data should be used in various scenarios. Yet such decentralized "knowledge co-creation" remains rare.
Moreover, throughout the entire process—from organizing and processing data to outputting and using it—there is little room for community involvement. How to best incentivize different participants in the crypto ecosystem to build a larger data network remains an attractive and achievable goal.
Therefore, we need not only efficient utilization of on-chain data but also decentralized ways to use it:
-
Elevate beyond traditional SQL queries, indexing, and non-real-time methods to smarter, more intelligent approaches;
-
Move away from centralized models like OpenAI toward greater transparency, trustworthiness, openness, and community-driven development.
This is precisely where Chainbase steps onto the stage.
Unifying all chains: the rise of the full-chain data network
With this context, Chainbase becomes easier to understand:
Building the world’s largest full-chain data network, aiming to integrate all blockchain data into a unified ecosystem and serve as the largest trusted, stable, and transparent data source in the AGI era.
Put simply: any data from any chain can be intelligently leveraged by anyone.
If you’re still struggling to grasp the concept of a "full-chain data network," let’s examine full-chain data more closely.
First, how "complete" is full-chain data?
Each chain has its own architecture and data. Chainbase acts like a unifier, integrating data from dozens of major L1/L2 blockchains—including BTC, ETH, EVM, and non-EVM chains—into one cohesive ecosystem.

Second, what exactly does this full-chain data contain?
Answer: everything related to blockchains.
That may sound too abstract. Breaking it down, the data includes several types:
-
Raw data: originally recorded on the blockchain, such as blocks, contracts, transactions...
-
Decoded data: extracted from raw data and converted into human-readable formats, e.g., transaction details across different DeFi protocols...
-
Abstracted data: higher-level data extracting key information and metrics, better suited for business analysis and decision-making—such as tokens, prices, inscriptions & runes—easier to understand or targeted for specific analysis.
It’s like cooking—you can use ingredients either raw or partially cooked (abstracted), depending on your recipe.
Notably, Chainbase ensures real-time availability of this full-chain data (refresh interval under 3 seconds), meaning not only can you choose your preferred level of preparation, but the ingredients stay fresh.
This level of data freshness is unmatched by most current crypto data projects.

Then, where does so much full-chain data come from?
For on-chain data, node operators or RPC providers from any blockchain can connect to the Chainbase network via the open data gateway in Chainbase’s product architecture, supplying the aforementioned data from their respective chains.
This forms Chainbase’s data ingress layer—the Data Accessibility Layer. Since implementation requires technical understanding, we’ll detail it later in our architecture analysis; here we focus only on functionality.
Finally, how large is this full-chain dataset?
According to public data from Chainbase’s official website, the network currently stores petabyte-scale data, processes 110–150 million full-chain data calls daily, and has cumulatively handled over 500 billion data calls.
These data calls originate from over 15,000 developers and 8,000+ crypto projects already collaborating with Chainbase.

Deep beneath the visible crypto world, a vast full-chain data network has already taken shape.
In terms of sheer volume, it rightfully claims the title of the largest full-chain data network. But where does the “network” aspect manifest?
From a holistic view, the previously mentioned Data Accessibility Layer plays a primary role, gathering all data across chains and serving as the entry point;
Secondly, unlike centralized processing seen with OpenAI or cloud providers, Chainbase establishes a token-incentivized, community-driven, multi-party collaborative structure for data processing;
Finally, after processing, the aforementioned on- and off-chain raw data becomes accessible within Chainbase’s network. Developers can build “manuscripts” on this data—defining, extracting, transforming, and processing on-chain data—to derive valuable insights.

Thus, full-chain data transitions from backstage to center stage through stages of collection, processing, presentation, and utilization; providing foundational ("Dao") support for data usage, with practical techniques ("Shu") including but not limited to:
Enabling wallets to manage and view assets across multiple blockchains from a single interface, improving user convenience;
Security: tracking attacks, issuing security alerts, and conducting deep security analysis to protect blockchain networks;
Social: building social platforms allowing seamless interaction and content sharing among users from different blockchains;
DeFi: enabling DeFi platforms to support cross-chain lending, increasing liquidity and flexibility.
Note these are just examples. As an infrastructure product, Chainbase enables these applications—but Infra can do much more.
Four-layer dual-consensus architecture: the solid foundation of the stage
For full-chain data to perform on stage, robust backstage support is essential.
Chainbase’s four-layer dual-consensus architecture effectively serves as four pillars supporting the stage—each layer fulfilling distinct roles to jointly enable full-chain data utilization while ensuring orderly operations behind the scenes.
Earlier, we briefly touched upon this architecture when discussing the full-chain network. Now, let’s analyze it in greater detail.
Since all of Chainbase’s operations revolve around data, let’s examine the four layers from bottom to top, following the flow of data ingestion, processing, and output:

-
Data Accessibility Layer: the entry point for full-chain data, solving how data enters the network.
-
Consensus Layer: when data state changes during processing, the decentralized network must reach agreement on those changes—a familiar "consensus flavor" in most crypto projects.
-
Execution Layer: since data processing tasks occur, various mechanisms must ensure they are executed securely and efficiently.
-
Co-Processing Layer: think of this as where processed data is delivered, involving questions of how data is output, who uses it, and for what purposes. “Co-processing” implies community collaboration to generate high-quality data for diverse applications.
From this logic, it’s easy to understand how data enters, gets processed, and is utilized. Chainbase’s four-layer architecture operates in harmony, each fulfilling its designated function.
Next, let’s break down each layer to understand their operational models and value.
-
Data Accessibility Layer: Rollup of full-chain data, secure integration of off-chain data
This layer serves as Chainbase’s data entry point.
For on-chain data, node operators or RPC providers from any blockchain can connect to the Chainbase network via the open data gateway in Chainbase’s architecture, submitting relevant data from their chains.
For off-chain data—such as social media user behavior—it can also enter the Data Accessibility Layer through trusted methods like ZK proofs via the open data gateway, then rolled up into the Chainbase network, preserving privacy while acquiring data.
Essentially, this functions like a decentralized data lake, aggregating data. ZKPs ensure submitted data is correct while protecting privacy; multi-node participation in storage and verification (SCP) ensures data reliability and decentralized organization.
-
Consensus Layer: CometBFT consensus mechanism provided by Cosmos ensures state synchronization
Every crypto product faces a classic challenge: how to agree on state changes in a fully transparent yet trust-limited environment?
In Chainbase, this translates to reaching consensus on changes in data processing states.
To achieve state consensus, blockchain presence and consensus algorithms are indispensable. Chainbase adopts Cosmos’s CometBFT consensus algorithm—we won’t dive deep into technicalities here.
What matters is that this is an improved Byzantine Fault Tolerance algorithm, tolerating up to one-third of faulty or malicious nodes, maintaining consensus even if some nodes act maliciously.
This tolerance threshold balances efficiency and resilience, ideal for achieving consensus under heavy data loads.
-
Execution Layer: EigenLayer + on-chain database ensures performance and adds economic security
When there’s demand for data calls in the Chainbase network, the Execution Layer comes into play.
Any data operation requires a “venue”—a database. Chainbase uses its proprietary Chainbase DB, an on-chain database designed for parallel processing of data and tasks, handling potential high-concurrency demands to ensure overall network performance and throughput.
But execution doesn’t guarantee sufficient security.
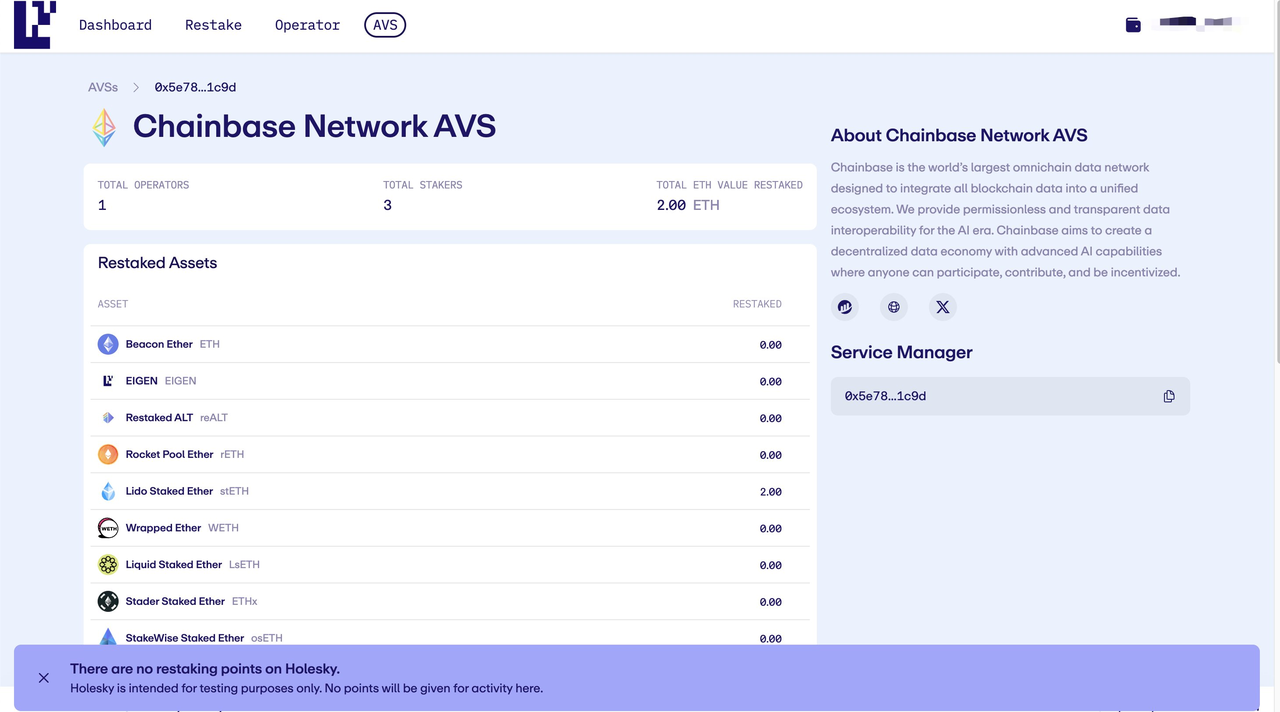
Hence, Chainbase’s solution is to obtain economic security from EigenLayer.
Leveraging EigenLayer’s restaking capability, Chainbase builds its Active Validation Service (AVS). This allows Chainbase to inherit the strong economic security from Ethereum stakers, securing its own data processing services.
-
Co-Processing Layer: community co-creation, multiple participants fulfilling distinct roles to maximize data value output
This layer feels closest to intuition, showing how data is used to create value.
In the crypto world, diverse applications generate vast amounts of varied data. Extracting value from these isolated, heterogeneous datasets is the challenge the Co-Processing Layer addresses.
Chainbase’s core idea here is enabling mass developer collaboration to accumulate knowledge and generate collective intelligence.
Concretely, this collaboration manifests as:
-
Knowledge contribution: users contribute their expertise in data processing and task modeling to the co-processor layer. This collaborative environment leverages collective intelligence to enhance network capabilities.
-
Knowledge assetization: the co-processor layer transforms knowledge contributions into assets, managing their distribution, circulation, and trading to ensure contributors are rewarded.
-
CBT token ecosystem: an integral part of the network incentive structure, facilitating payments, settlements, staking, and governance—details covered later.
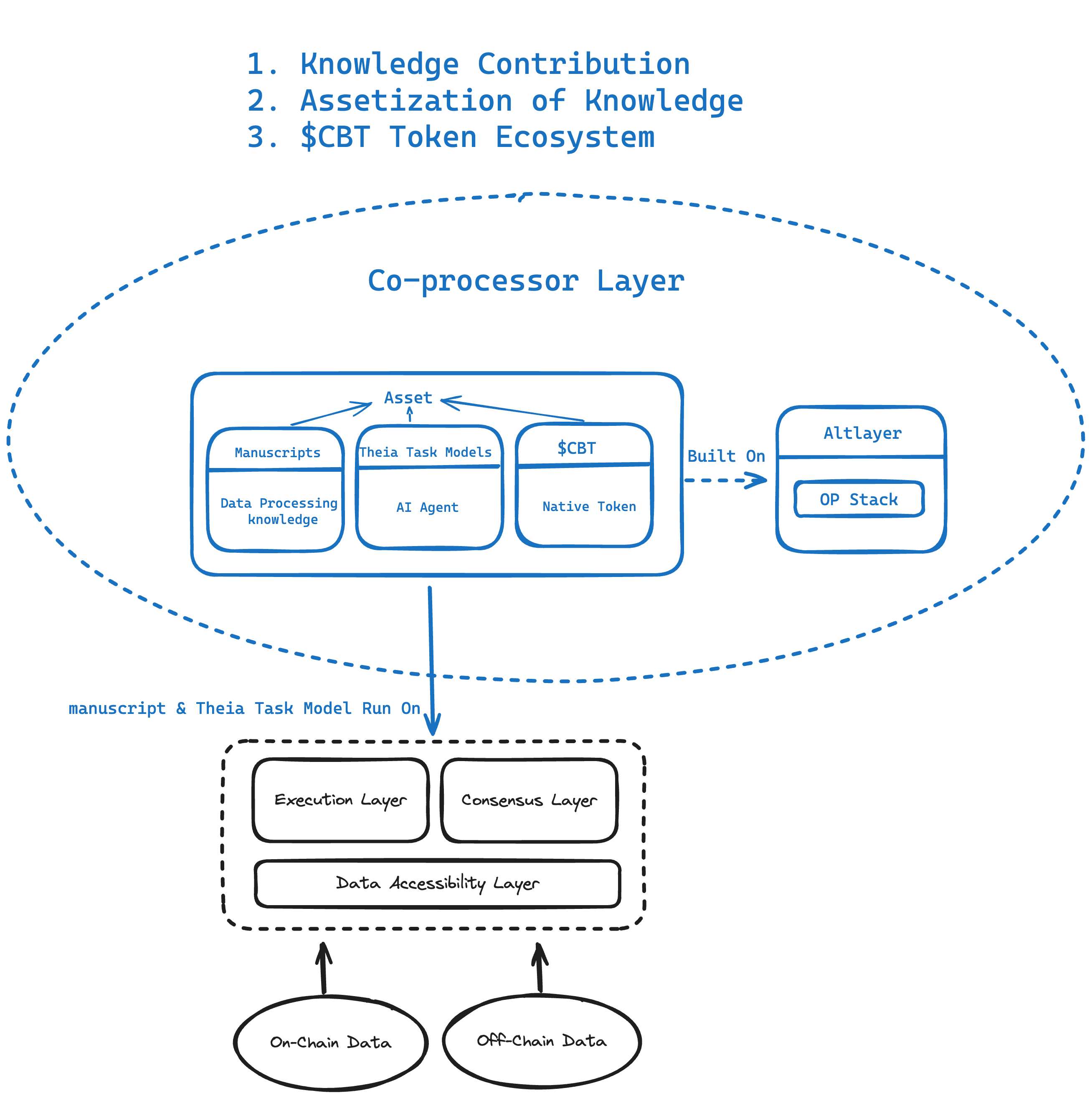
Simply put, the Co-Processing Layer enables outcomes like creating a “recipe” for analyzing on-chain phishing scams. Developers identify required data, package it into templates for broad use.
Lastly, ordinary users also have a place in the Chainbase network.
Average crypto users may lack data analysis skills, but they can interact with the Chainbase network using natural language to gain insights and intelligence about the crypto world.
Visually, this resembles a crypto-native ChatGPT—but it’s not just a skin over GPT’s core. Instead, Chainbase delivers a powerful offering for regular users at the Co-Processing Layer:
Theia: a crypto-native AI large language model trained on massive full-chain data.
While handling data operations, Chainbase trains Theia using 7 billion general-purpose LLM parameters plus 200 million crypto-specific parameters.

Note: “crypto-native” means shaping an agent capable of real-time perception within the crypto world—understanding what’s happening moment by moment in areas where GPT cannot reach.
While GPT wrappers work, they cannot understand native crypto context or deliver real-time, low-latency crypto-native content.
Most current AI uses of on-chain data involve feeding schemas to AI to help write SQL queries—still stuck at the non-intelligent querying stage, essentially an upgraded version of indexing.
Theia’s approach, however, is fundamentally intelligent—leveraging vast on- and off-chain data for efficient thinking, analysis, and response, exhibiting proactivity, creativity, and real-time responsiveness, placing it in a different league from current on-chain data products.
Thus emerges a large language model better suited to the crypto-native audience.
Soon, informational advantage may no longer be exclusive to crypto “scientists.” Theia democratizes AI intelligence, enabling ordinary people to leverage the sophisticated full-chain data network.
By linking the crypto-native LLM Theia with external resources (RAG), generative AI delivers more accurate responses.
Users interact with a friendly Q&A interface to receive intelligent responses—based on learning encryption patterns from extensive on- and off-chain data and temporal-spatial activities, including causal reasoning about crypto patterns.
For example, when casually asking “What are the trending DeFi protocols lately?”, Theia handles defining “trending,” substantiating it with data, sorting and presenting results—all delivering a final synthesized answer.
Meanwhile, data scientists can use Theia to build task models—teaching others how to fish. For instance:
-
Security task model—focused on security, e.g., AI assessing crypto vulnerabilities, real-time threat monitoring, compliance audits
-
Trading task model—analyzing market trends, optimizing strategies, risk management
-
Sentiment task model—tracking social media sentiment, trend热度, event impact, etc.
When it comes to AI capabilities, teaching someone to fish beats giving them a fish.
Based on available information, Theia can do everything existing crypto AI products can do, backed by massive data and model optimization—a “teach to fish” approach rather than handing out isolated solutions for specific scenarios.
Moreover, the Co-Processing Layer shows how full-chain data collaborates to let the crypto-native model Theia perform its dance of intelligence. The way crypto users access information, intelligence, and insights may soon be disrupted and revolutionized—AI helping crypto evolve for the better.
-
Dual Consensus Across Layers: prioritizing efficiency and security while balancing economic incentives
After understanding Chainbase’s four-layer architecture, the dual-consensus design becomes clear.
By incorporating Cosmos and EigenLayer, Chainbase strengthens guarantees around both data processing itself and agreement on state changes.
EigenLayer operates at the Execution Layer, where AVS handles execution tasks, inheriting Ethereum’s economic security. Cosmos operates at the Consensus Layer, using an optimized BFT algorithm to reach agreement on data state changes with fault tolerance.

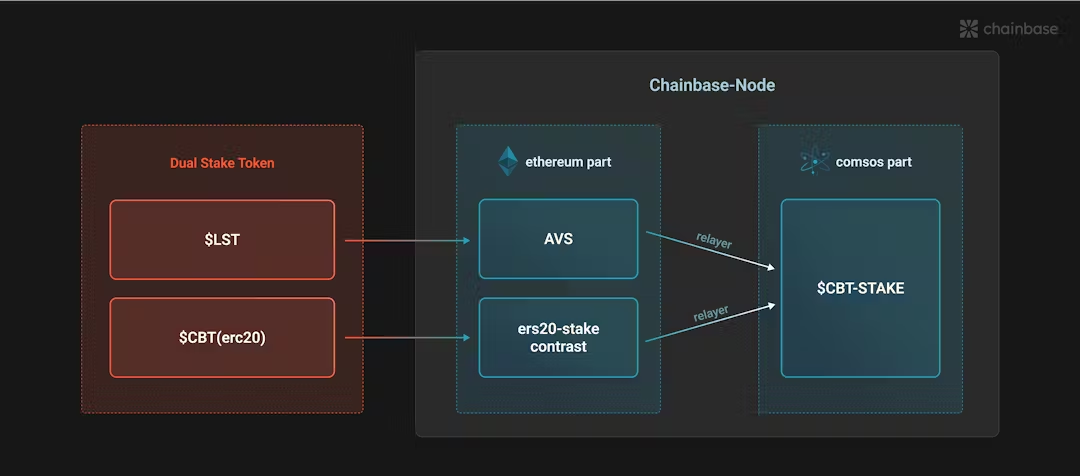
More importantly, the dual-consensus design naturally introduces a dual-token staking mechanism, mitigating the death spiral problem in traditional POS networks:
Typically, when a project’s single token loses value and uses a POS design, network security declines as staked TVL drops. Worsening fundamentals further depress token price, creating a vicious cycle of deteriorating security.
With dual-consensus, Chainbase accepts both its native CBT token and various LST tokens from the Ethereum ecosystem for staking—enhancing economic security, unlocking LST asset value, and attracting external liquidity.
Although the official hasn’t announced TGE timing or detailed tokenomics yet, the utility and functions of the CBT token are already clear, offering reference points for research.
In short, CBT is the key economic incentive ensuring all network participants fulfill their roles.
-
Chainbase network operator nodes ensure smooth data processing tasks, earning 80% of data query fees (users pay to use Chainbase’s data network) + 100% of rewards from the operator pool (funded by Chainbase);
-
Validators verify transactions, ensure data integrity, and maintain network stability, earning 100% of block rewards;
-
Developers/data scientists: write manuscripts to enable effective data processing and querying, improve data logic, earn 15% of data query fee rewards;
-
Delegators: stake tokens to validators and operators to share rewards, similar to income from Ethereum delegation protocols.
Overall, Chainbase’s four-layer dual-consensus architecture is the core of the entire data network, enabling smooth, efficient data processing while balancing economic incentives and security.
An elegant, self-consistent, and clear design, laying a solid foundation for the full-chain data network’s grand performance. Especially noteworthy is the Co-Processing Layer’s cultivation of a crypto-native AI model, elevating data utilization to new heights and broader horizons.
From data to wisdom delivery: crypto and AI empowering each other
After studying Chainbase’s product, I believe it is undergoing a role transformation—from a pure data provider to a full-chain data network supporting AI.
This transformation isn’t just a vague narrative shift—it signifies a firmer step forward in how crypto-world data is utilized.
From the product, you clearly sense it’s not just providing data, but actively creating conditions for intelligent data use and wisdom generation.
In knowledge management, there’s a classic DIKW model (shown below) illustrating hierarchical knowledge acquisition—prompting deeper reflection on how the crypto industry leverages data and information:

From this model, most current crypto projects merely provide data and information, falling far short of generating knowledge and wisdom;
Proactivity and creativity represent the ultimate goal of on-chain data utilization. While AGI-era GPT-4 already delivers knowledge and wisdom, crypto data utilization still has a long journey ahead.
From data → information → knowledge → intelligence, crypto data can make AI better, while AI enhances crypto operations with greater insight and efficiency.
Crypto and AI were perhaps meant to empower each other.
Regarding Chainbase itself, I hold even greater expectations.
Currently, the project already possesses substantial data volume, Theia model shows promise, and official Twitter indicates testnet progress at 50%, with mainnet launch expected within the year;
The power of full-chain data awaits further unleashing. Chainbase might bring a Pareto improvement to the crypto world:
A global efficiency upgrade across crypto, without sacrificing any individual party’s interests.
In this new paradigm of crypto data utilization, no one is a loser.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News













