2023 Solana Developer Ecosystem Report
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

2023 Solana Developer Ecosystem Report
Today, the Solana developer ecosystem boasts over 2,500 monthly active open-source library developers, with a steady influx of professional developers joining the ecosystem, making the development environment increasingly mature.
Written by: Solana Foundation
Translation: 0x711, BlockBeats
The Solana developer ecosystem continues to grow. In 2023, significant progress was made in tools, developer experience, content quality, and the diversity of available programming languages. Today, the Solana developer ecosystem boasts over 2,500 monthly active open-source library developers, with a steady influx of professional developers joining, making the environment increasingly mature.
Developer Ecosystem
The health of any blockchain’s developer ecosystem is critical for sustaining the network. While measuring ecosystem health is difficult and no single metric tells the whole story, the following indicators are essential for evaluation:
-
Total number of monthly active open-source developers: Open-source developers actively building within the ecosystem each month.
-
Developer retention rate: The ecosystem's ability to foster sustained, "sticky" development.
-
Developer experience level: The professional expertise of developers.
-
Developer growth: The number of developers entering the ecosystem at any given time.
Total Monthly Active Developers
One of the simplest ways to measure how a network grows is the number of active developers on the blockchain. At the Solana Foundation, we use an open-source service to collect developer data and have publicly documented our methodology. Over the past year, Solana has had approximately 2,500–3,000 developers consistently active throughout 2023.
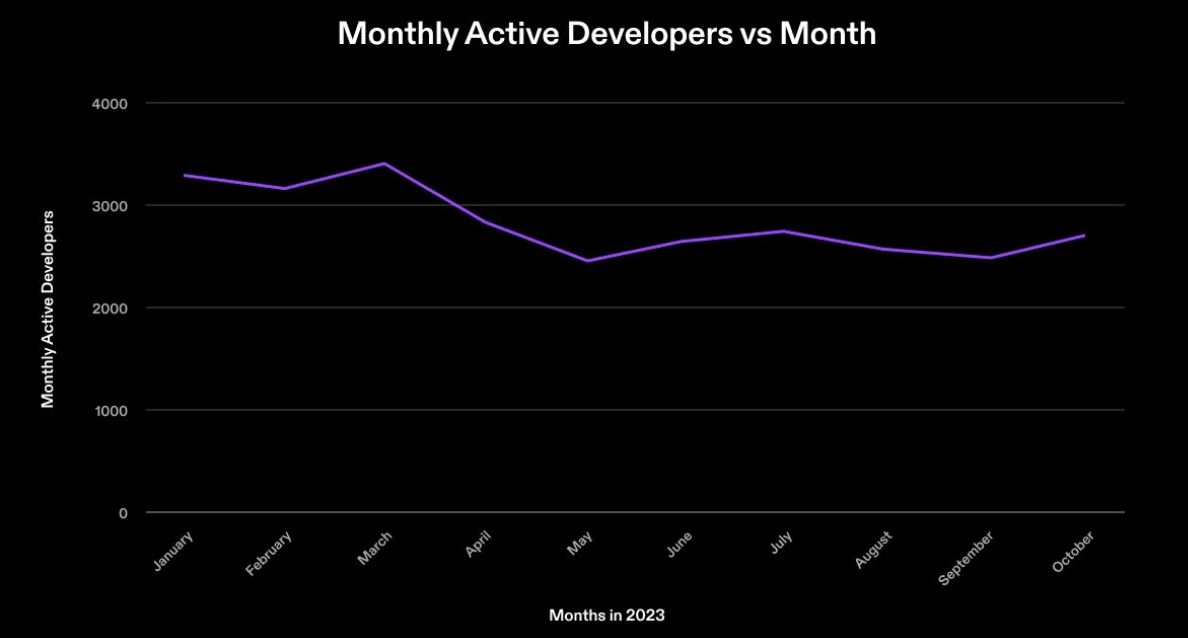
Monthly active developer data for 2023
Maintaining a consistent base of developers is a key indicator of a healthy ecosystem, as it demonstrates the ecosystem’s ability to attract and retain new talent. Note that this data only counts developers who contribute to public repositories and does not account for activity in private repositories, which may lead to underestimation at certain points in time. The Solana Foundation remains committed to supporting the growth of the open-source community on Solana; continued support for public development will help drive future innovation in Solana applications.
Developer Retention Rate
Measuring monthly active developers is only part of the story. A large number of experimental developers may not translate into a sustainable developer community if retention rates are low. Low retention poses risks, potentially leading developers to leave before making meaningful contributions to the network. To further assess the health of the developer community, it is crucial to measure retention alongside monthly active developers. For this report, a developer is considered retained if they make at least one code commit in each of three consecutive months after starting.
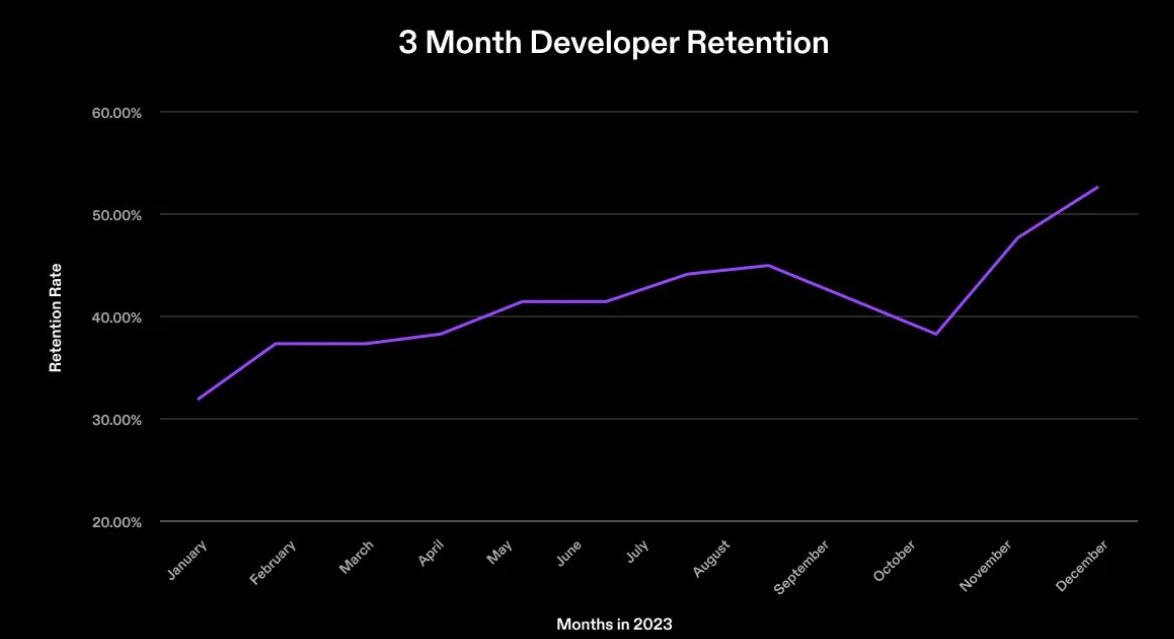
Monthly developer retention rate data for 2023
In 2023, the three-month developer retention rate in the Solana ecosystem improved from 31% to over 50%, meaning more incoming developers stayed within the ecosystem. This improvement in retention can be attributed to several factors:
-
Onboarding experiences are improving.
-
Solana has become a clearer choice for developers.
-
Opportunities within the ecosystem have increased.
Over the past year, the Solana developer onboarding process has steadily improved, with the Solana Foundation releasing multiple new guides on how to get started. Through various developer bootcamps with differing focuses and difficulty levels, 400–500 advanced developers graduate every six months intending to build on Solana. Data from the latest Solana Hyperdrive hackathon shows that about 50% of the top 150 submitters and 50% of winners completed one of these bootcamps. Teams across the ecosystem also strongly support building on Solana—for example, the Helius team published articles explaining why developers should choose Solana. While opportunities for developers within the ecosystem are hard to quantify, the number of jobs posted on jobs.solana.com—a site aggregating roles across the Solana ecosystem—has steadily increased, from 15 in January 2023 to 95 at the time of publication, with 41 added just in December 2023 alone. While imperfect, job availability is important for keeping new talent contributing to and building on the network.
Developer Experience Level
The skill level of developers building applications on-chain directly impacts the overall success of the network. If a network is primarily built by more experienced developers, its applications are more likely to attract new users. On Solana, over half of the developers entering the ecosystem have at least three years of experience, enabling them to make more sophisticated contributions to applications built on the network. One way to measure this is by assessing the experience level of attendees at Solana Hacker Houses—week-long events held globally. These events serve as spaces for learning and networking, with lectures and office hours specifically tailored for developers and founders. Among the 1,059 developers who attended Solana Hacker Houses in 2023, 52.5% reported having more than three years of development experience—more than any other group at our events.
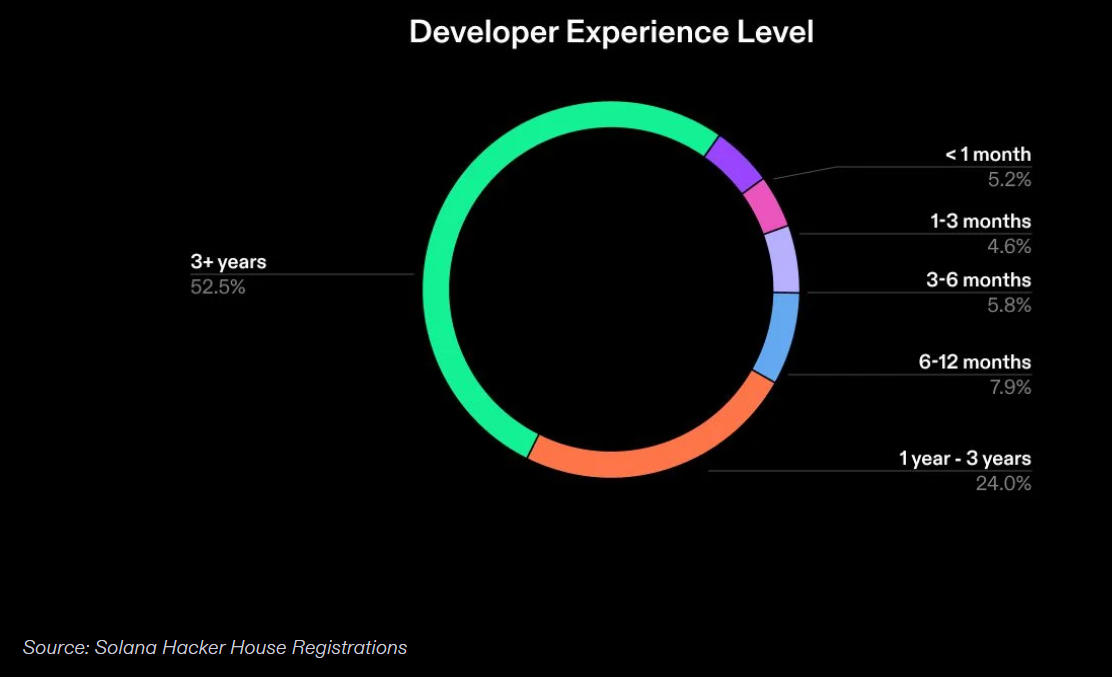
Developer experience level data
Developer Growth
Although the Solana ecosystem is relatively new (Solana’s mainnet beta launched in March 2020), its developer ecosystem has grown into the second-largest by total number of monthly active developers. This growth stems from many different factors, and it is difficult to pinpoint exactly what attracted most developers. Since mainnet beta launch, the Solana Foundation has initiated or funded various initiatives aimed at growing the developer ecosystem. Key programs include Solana hackathons, Solana Hacker Houses, Breakpoint, educational bootcamps, and sponsored university events. Ecosystem-led teams such as SuperteamDAO, mtnDao, Metacamp, and Gen3 have also contributed significantly to this growth. We expect Solana hackathons to remain a key indicator of ecosystem health. Since 2020, the Solana Foundation has sponsored eight hackathons. Over the past three years, more than 3,000 projects have launched, raising over $600 million in funding from hackathon submissions. Project submissions have increased with each event—the most recent hackathon, “Solana Hyperdrive,” received over 900 submissions.
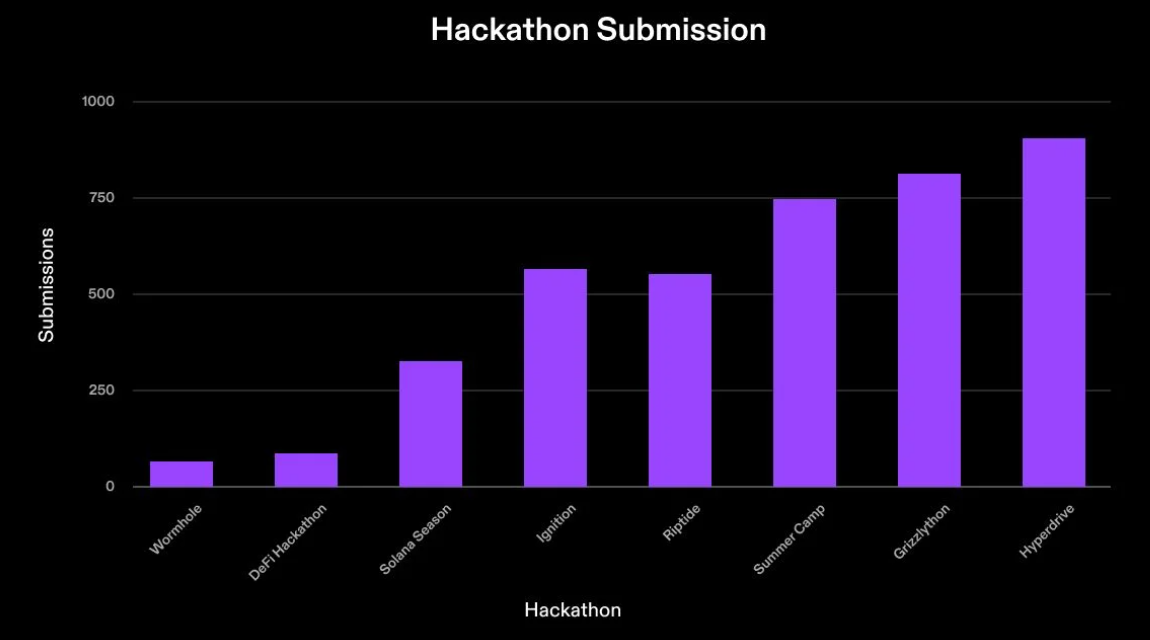
Hackathon submission count
Global Growth
It's important to note that while the entire ecosystem is growing, much of the growth comes from newly engaged global regions. This global expansion of the developer ecosystem stems from bottom-up community-driven efforts. An example is SuperteamDAO, a builder community focused on India, which began expanding to other countries in early 2023 and now has chapters in eight nations. Other groups adopting similar models include Gen3 in Taiwan, MetacampDAO in Singapore, and mtnDao in the U.S. While the Solana Foundation does not currently track granular regional growth daily, Solana hackathons held every six months provide visibility into regional growth trends. The most recent hackathon, “Solana Hyperdrive,” included participants from 151 countries, with final submissions from 65.
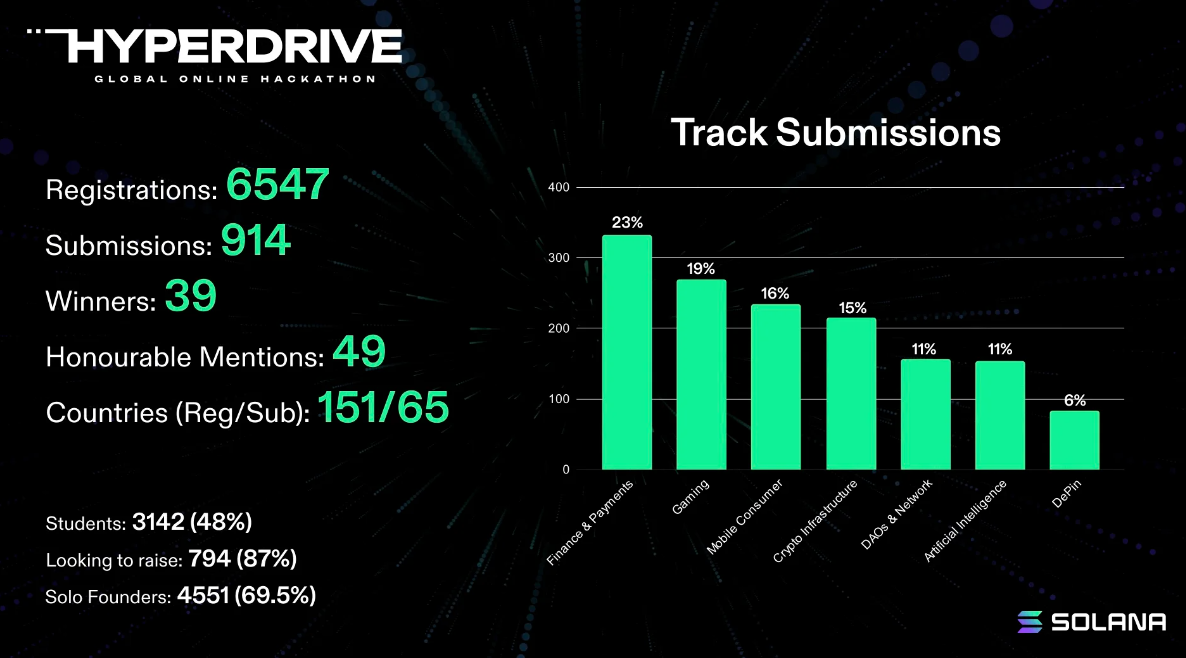
Historically, the United States has been the most represented country in Solana hackathons, followed by India. In recent years, the share of submissions from outside the U.S. has risen sharply—from 76% in 2021 to 91% in Hyperdrive. Developer communities in countries with deep engineering talent pools—such as India, Germany, China, the UK, Turkey, and Vietnam—remain priority focus areas. Countries to watch include Brazil and Latin America, Japan, France, Nigeria, and Israel.
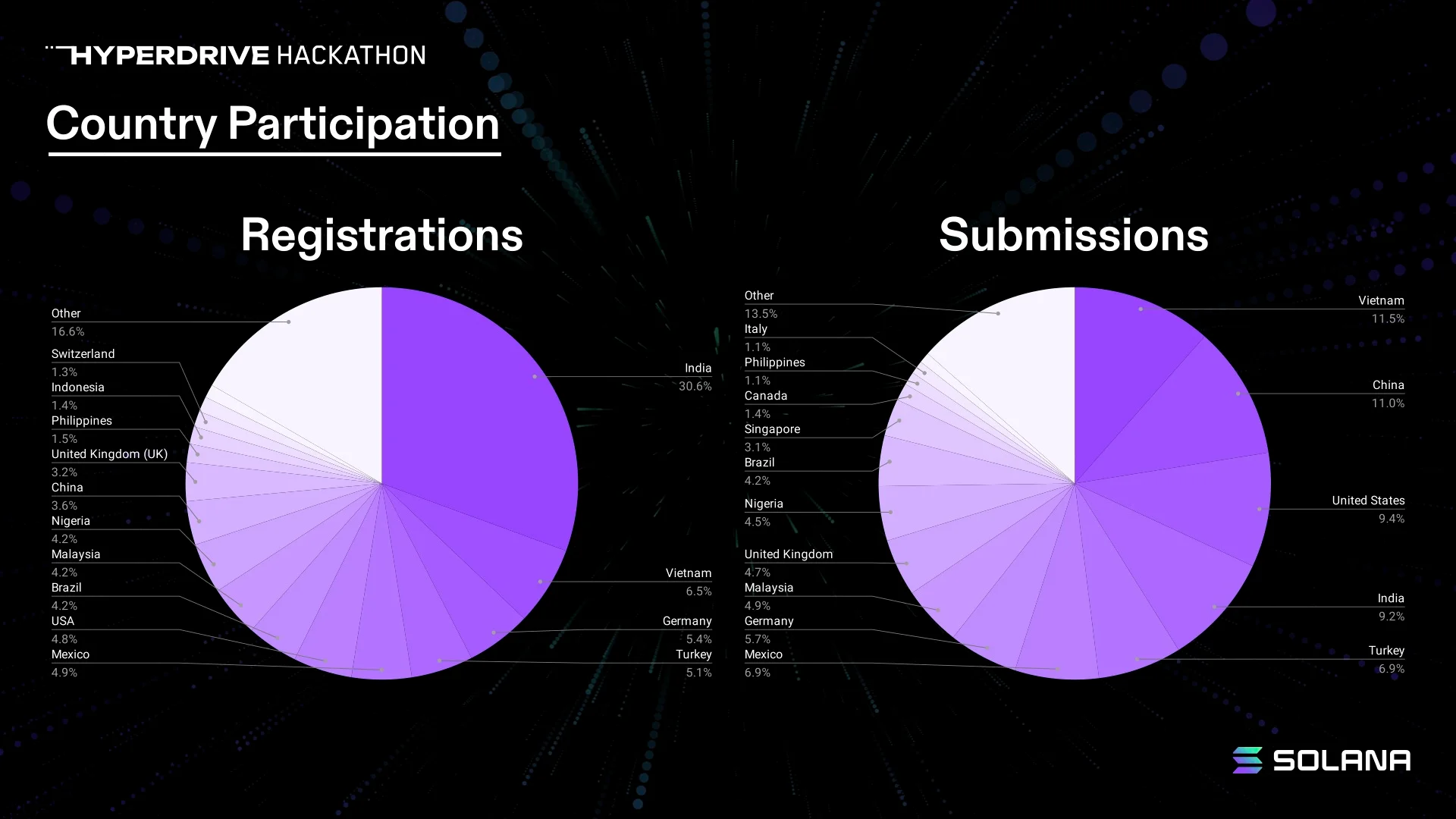
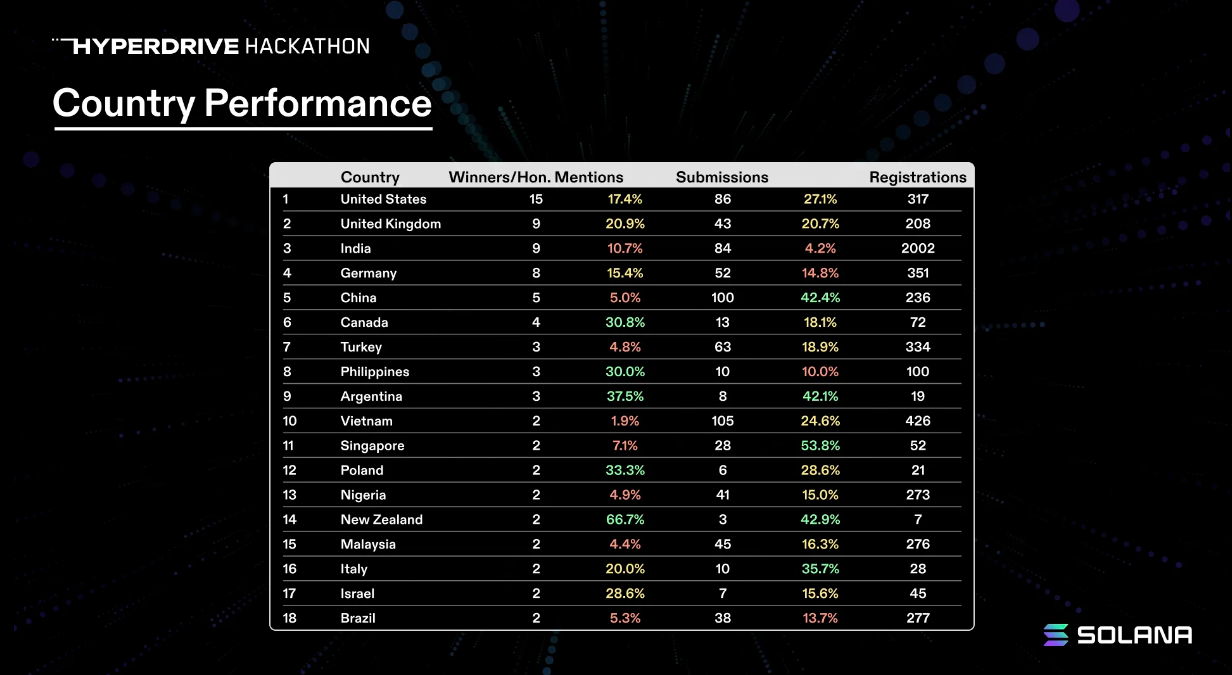
As the most mature region in the Solana ecosystem, the U.S. still dominates among hackathon winners, but these numbers continue to shift. Ultimately, the goal for any developer ecosystem should be high-quality projects evenly distributed worldwide.
Building on Solana Today
Widespread blockchain adoption depends on the availability of robust infrastructure and developer tools that enable seamless onboarding and continuous development. When choosing an ecosystem to build on, developers consider several key factors:
-
Developer experience: How easy is it to learn and build applications?
-
Maintenance: How much effort is required to maintain and monitor applications under development? As the Solana ecosystem continues to evolve, each of these areas is expected to mature and become more accessible to developers.
Developer Experience
Developer experience is a critical component of any ecosystem—the maturity of available resources and tools decisively influences the development process. Today, the Solana blockchain offers an increasingly mature tooling ecosystem and a wealth of onboarding resources for new developers. Looking ahead, publishing more end-to-end project-building resources could accelerate onboarding for new developers, along with better debugging tools and tools for understanding compute resource usage. The Solana protocol is known for its parallel processing capability, which is achieved by requiring developers to pre-declare the state segments they are using. Therefore, developers need appropriate frameworks and tools to manage state more easily. Developers considering whether to build on Solana typically ask the following questions:
-
Documentation and examples: How easy is it to reference available documentation and resources?
-
Education programs and courses: What educational opportunities are available to developers?
-
SDKs and frameworks: Are there commonly used SDKs and frameworks to accelerate my development?
-
Local development tools: How flexible are local tools for quickly prototyping a new application?
-
Tool completeness: How does Solana compare to other ecosystems?
Documentation and Examples
Currently, documentation on the Solana blockchain is largely conceptual and includes guides to help developers get started. Over the past year, numerous program examples have been created to assist anyone in building on-chain applications on Solana, helping to kickstart the on-chain developer ecosystem. The Solana Cookbook provides a comprehensive selection of client-side code examples, including hundreds of code snippets, each available in at least three different programming languages. For developers seeking deeper insights into the latest internals of the Solana protocol, up-to-date information is currently limited—partly due to the rapid pace of protocol updates. Solana’s documentation and protocol specifications will gradually improve, with missing sections being filled in prior to implementation. As Solana matures, more research organizations like Umbra Research are beginning to document internal knowledge, making such information more widely available in official documentation.
Education Programs and Courses
At the time of writing, a variety of complete education programs and courses are available to help developers enter the Solana ecosystem. These include self-paced courses and mentor-guided, cohort-based programs. The diverse structures of educational development programs allow developers to learn in their preferred way, maintain high accountability, and increase the likelihood of participant success. Self-paced educational programs and courses from the past 12 months include:
-
Unpacking Solana Course
-
Freecodecamp
-
EasyA - IdeaSoft
Additionally, some mentor-guided programs include:
-
Web3BuildersAlliance
-
Encode Club
-
Ackee Blockchain
-
Narr8ive
-
Calyptus
-
DevsNest
-
RiseIn
-
Nas Academy
SDKs and Frameworks
The Solana developer ecosystem has a solid foundation of SDKs that impact most developers. In terms of UI frameworks, there is a strong concentration around React and Next.js tools on the Solana blockchain. For each language, available tools can be assessed as follows:
-
Solana SDK: SDKs for interacting with RPC and creating transactions to communicate with the blockchain.
-
Program frameworks: Tools for creating Solana programs using specific programming languages.
-
Developer impact: Measured by the percentage of developers using a particular programming language or UI framework.
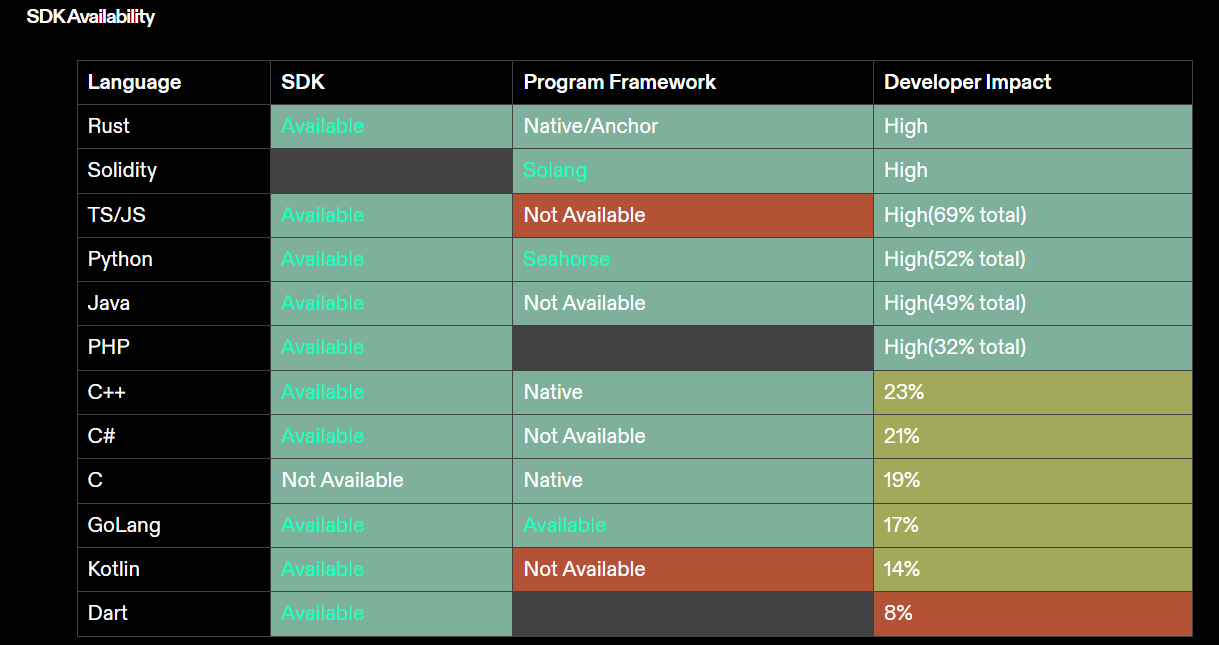
New developers entering the ecosystem can now fully participate in building on Solana by writing only TypeScript—without ever needing to learn Rust or write Solana smart contracts. Moreover, new tools are now available for developers across different technical domains. Game developers have fully functional Unity SDK, Godot SDK, and Unreal Engine SDK. Fintech developers can rapidly adopt Solana through SolanaPay. Building on Solana has never been easier.
UI Frameworks
Scaffolds and wallet adapters enhance the developer experience for each UI framework. Currently, React and Next.js are the most widely supported frameworks, covering a large portion of developers.
-
Scaffold: A tool that allows developers to quickly set up boilerplate websites.
-
Wallet adapter: Tools that support easy integration with Solana wallets.
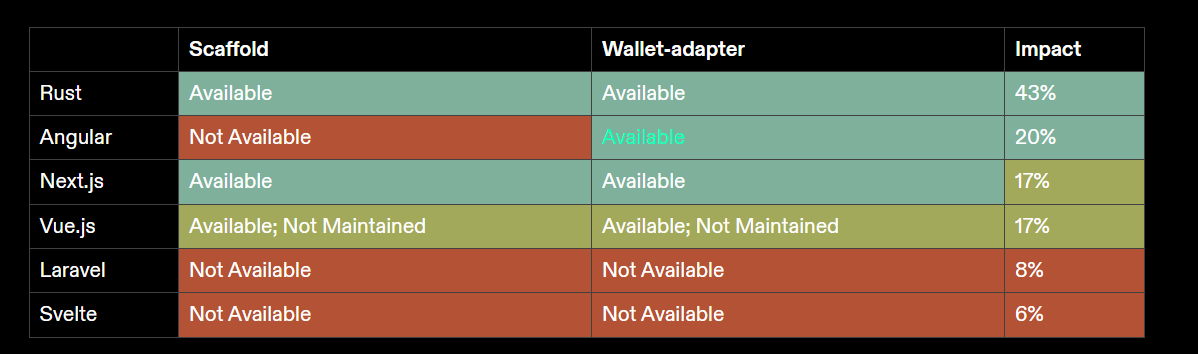
Local Development Environment
The local development environment is a collection of tools that allow developers to build locally on their machines, accelerating development and reducing overhead. To build a new application, developers must first start locally. An efficient local development environment can significantly reduce friction when building on a new framework. The primary local environment tool currently used is the Solana Tool Suite. It enables developers to run test validators on their local machine, send transactions, airdrop tokens, deploy smart contracts, and run tests against the environment. This suite allows developers to run applications end-to-end in a production-like setting. Compared to EVM’s mature Foundry toolchain, the Solana Tool Suite supports CLI transaction sending and easy replication of mainnet accounts, though the experience is less streamlined. Pulling accounts is more manual than Foundry because Solana smart contracts are stateless, meaning users must gather or create state across many locations to run local tests. Sending transactions is possible, but not as seamlessly scalable to any smart contract due to Solana’s protocol design, which gives users choice in serialization during interactions—leading to varied interaction patterns without a direct standard. Both limitations are addressable over time.
Parity with Other Ecosystem Toolchains
One way to assess the availability of tooling in the Solana ecosystem is to compare it with popular tools outside EVM. Most developers new to web3 and smart contracts learn Solidity as their first language and adopt EVM programming paradigms. This initial exposure to EVM complicates later transitions to the Solana ecosystem, as it often requires unlearning EVM concepts to properly develop using Solana’s account model. Out of 5,800 monthly active Solidity developers, only 7% have tried Solana development. Some tools already exist to accelerate adoption of the Solana blockchain and speed up developer migration from EVM:
-
Neon: EVM-compatible development environment
-
Hyperledger Solang: Solidity compiler for Solana
Beyond EVM-compatible environments, many developers may opt for native Solana development practices. For most major tools available in the EVM ecosystem, there is a Solana equivalent:
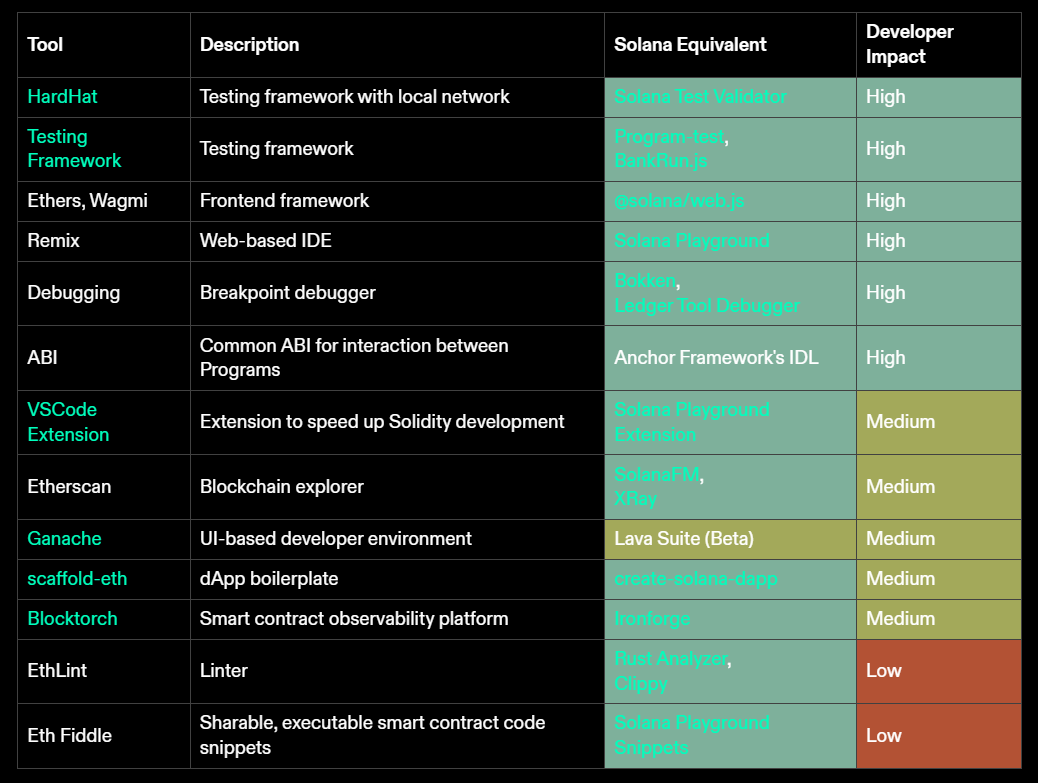
Given Solana’s relative youth compared to EVM, this demonstrates that the developer ecosystem is building all necessary tools to improve the Solana developer experience. While not yet matching all standards of Foundry, the Solana ecosystem is well-positioned to further refine and mature its toolchain.
Maintenance
Any developer deploying an application to production knows that easy maintenance prevents many headaches. How does the Solana protocol fare in maintaining applications? The ease of maintaining an application depends on several factors:
-
Testing and debugging: How simple is it to write tests to maintain functionality and debug potential issues?
-
Security: How to keep the application secure?
-
Analytics: How to properly monitor application performance in production?
Testing and Debugging
Testing and debugging are vital in the development lifecycle. Tools related to testing and debugging can save hours of development time, help companies identify issues faster, and reduce risks during builds. In 2023, the developer ecosystem built tools that made testing and debugging simpler.
-
Debugger: Over the past year, two methods for step-through debugging were introduced—Bokken and the ledger-tool debugger. These tools allow you to set breakpoints at each line of code in basic Solana smart contracts and inspect account states at each point.
-
Testing: Mocha testing via the Anchor framework is currently the most widely used testing framework for Solana smart contracts. In the past six months, Solana Bankrun was created, greatly speeding up tests and enhancing testing capabilities. Solana-program-test also exists, offering similar features and speed.
-
Code coverage: Code coverage tools for Solana smart contracts remain incomplete. Developers can use general Rust code coverage tools, but most fail to accurately measure coverage.
-
Logging: Most commonly, the basic Solana logger used in solana-program. Logs can be retrieved via smart contract logs and transmitted through Geyser or sologger for analysis. SaaS tools like Ironforge can also help monitor application logs in production. Over the past year, the basic logger has been improved via the Anchor framework, overcoming many earlier limitations.
-
Events: The Anchor framework currently provides a very basic way to handle events for Solana on-chain applications. However, without additional infrastructure, the framework does not offer an instant event queue or allow catching up to the chain’s latest state without extra setup. There are future proposals to improve event handling on Solana.
Security
For any company aiming to operate securely, having a secure application in production is crucial. Security in decentralized applications is even more critical—any vulnerability in a smart contract, if not handled carefully, could lead to massive financial loss. So how do developers today keep their smart contracts secure?
-
CI scanning: Developers can use basic GitHub Actions scans to detect small vulnerabilities in smart contracts. Such scans help quickly identify issues before any deployment.
-
Audits: Any serious smart contract developer undergoes audits by third-party firms within the ecosystem. In just a few years of Solana development, multiple companies specializing in audits have emerged.
-
Fuzz testing: Proper fuzz testing against common known vulnerabilities is a good way to keep smart contracts secure. Fuzz testing frameworks like trdelnik offer a quick way to assess whether a smart contract is vulnerable to simple threats.
-
Real-time scanning: While running in production, actively guarding against potential threats by real-time scanning of transaction anomalies is ideal. Riverguard offers high-level scanning on mainnet, analyzing a range of transaction patterns to determine if on-chain applications are vulnerable to attacks.
The Solana developer ecosystem offers a substantial set of tools to keep on-chain applications secure in production. However, as developer skill levels rise, more sophisticated attacks also increase—continuous improvement in applications, security education, and tooling remains essential for long-term success.
Analytics
Developers seek analytics on their application’s performance and that of competing applications. Currently, analytics platforms support Solana via raw and parsed transactions. Due to insufficient depth and availability of data in IDLs, analytics platforms are slowed down and unable to deliver rich account-level analysis. Once the IDL framework provided by Anchor is improved and more widely adopted, smart contract analytics will also improve.
Future Opportunities
The Solana developer ecosystem is only four years old. In this time, abundant content and tools have nurtured today’s maturing ecosystem. Many opportunities remain. Going forward, the developer ecosystem must further refine the local development environment to match Foundry’s best-in-class tools, add stronger event systems, and provide more end-to-end product examples to accelerate new application development. The Solana Foundation continues to support the growth of the Solana developer ecosystem, encouraging new developers to contribute to developer experience and supporting tool maturity. If you have ideas for improving the Solana developer ecosystem and need financial support, please apply for a grant. We welcome any feedback on the developer ecosystem and how to improve the experience.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












